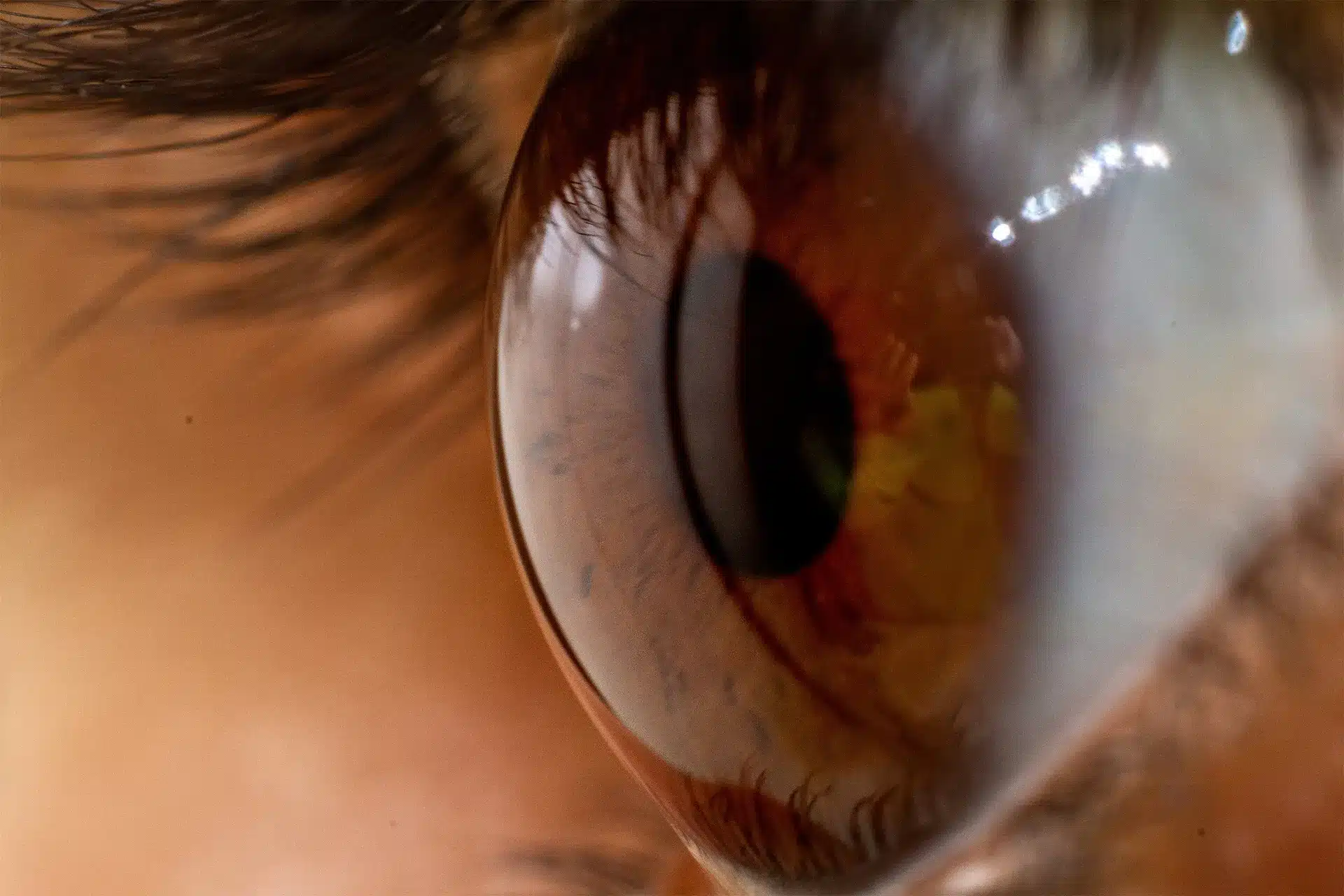
Posterior subcapsular cataracts (PSCs) are a specific type of cataract that develops at the back of the eye’s lens, just inside the lens capsule. Unlike other cataract types, PSCs form in a critical area known as the eye’s “nodal point,” where light converges as it enters the eye. This unique location makes PSCs particularly disruptive to vision, even when they appear relatively small.
What Are The Symptoms Of Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts?
PSCs can cause significant visual impairment due to their positioning. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred vision, especially when reading or focusing on close objects,
- Increased sensitivity to glare, particularly in bright light conditions,
- Difficulty with night vision,
- Halos around lights,
- Reduced contrast sensitivity.
If you experience any of these, it’s time to consult an eye care professional as early detection can lead to more effective management and treatment options.
Impact on Daily Activities
Many patients with PSCs report losing confidence in night driving due to increased glare from oncoming headlights. This loss of independence can significantly affect quality of life, making timely diagnosis and treatment crucial.
What Causes Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts?
While aging is a common factor in all cataract types, PSCs are more frequently associated with specific conditions and risk factors:
- Diabetes, especially Type 2,
- Prolonged use of corticosteroids or long-term steroid use,
- Exposure to radiation,
- Excessive UV exposure,
- Eye trauma or history of eye surgery,
- Intraocular inflammation or uveitis,
- Retinitis pigmentosa,
- Extreme nearsightedness,
- Certain genetic factors.
How Do Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts Form?
PSCs develop when lens fibers become overactive and form new growths beneath the lens capsule. This process causes older fibers to scatter, creating a cluster in the subcapsular region that interferes with vision. Unlike other cataract types, PSCs can progress relatively quickly, making regular eye check-ups essential for early detection.
Rapid Progression
PSCs often progress faster than other types of cataracts, leading to more rapid deterioration of vision. This means that patients may notice a significant decline in their vision over a short period, necessitating earlier surgical intervention.
Can Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts Be Prevented?
While complete prevention of cataracts is not currently possible, certain lifestyle changes can help slow or even prevent their progression:
- Wearing UV-protective sunglasses
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants
- Managing diabetes and other systemic conditions
- Avoiding prolonged steroid use when possible (under medical guidance)
- Regular eye examinations for early detection
How Are Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of PSCs typically involves:
- Comprehensive eye examination
- Visual acuity tests
- Dilated eye exam
- Slit-lamp examination (the gold standard for PSC diagnosis)
- Ophthalmoscopic examination
These tests allow eye care professionals to assess the extent and impact of the cataract on vision.
How Are Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts Graded/Classified?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has simplified the grading system for cataracts to encourage standardized evaluation. For PSCs, grading is based on the vertical diameter of the opacity. Only the most clearly visible opacities with distinct borders are considered in cases of multiple PSCs.
How Are Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts Treated?
When PSCs significantly affect vision and daily activities, surgery is often recommended. The primary treatment involves:
- Phacoemulsification: A minimally invasive procedure that uses ultrasound to break up and remove the cloudy lens.
- Intraocular lens (IOL) implantation: Replacement of the removed lens with an artificial lens.
Premium IOLs
For patients with PSCs, premium intraocular lenses (IOLs) can offer additional benefits:
- Multifocal IOLs: Provide clear vision at multiple distances, reducing the need for glasses.
- Toric IOLs: Correct astigmatism for clearer vision.
- Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) IOLs: Provide a continuous range of vision, from near to far.
Modern cataract surgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia, with a quick recovery time.
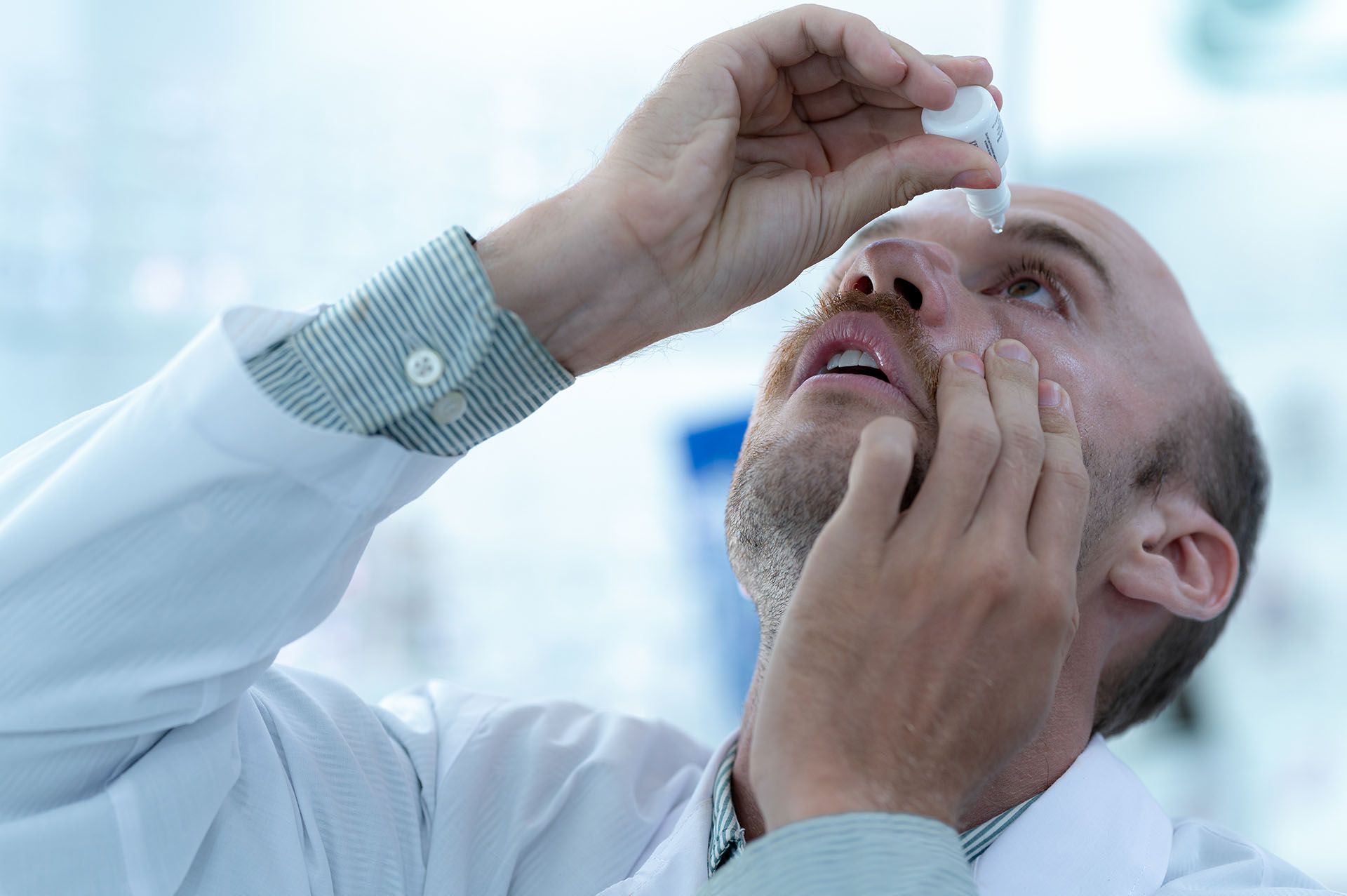
Post-Surgery Care
After surgery, patients are prescribed eye drops and given instructions for proper care. Most individuals experience improved vision shortly after the procedure, with complete recovery within a few weeks.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts: Treatability and Advancements
Posterior subcapsular cataracts, while potentially more visually disruptive than other cataract types, are highly treatable. With advancements in surgical techniques and IOL technology, patients can expect excellent outcomes and restored vision quality. Regular eye examinations are key to early detection and timely intervention.
Your Clear Path to Better Vision Starts Here
Visit https://bestcataractsurgeons.com/ to find top-rated cataract surgeons in your area and take the first step towards clearer, brighter vision.